I have an opportunity to work with my databases remotely from my computer without having to login to our dashboard. Here’s a how-to for PostgreSQL users.
Create Environment
The database can be accessed either via public IP or Cloudjiffy Endpoints (no public IP required). Let’s take a look at both options of creating database environment.
Environment with Public IP
1. Log onto Cloudjiffy.
2. Click the New Environment button at the top left of the dashboard.
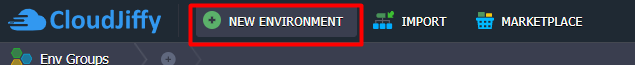
3. In the Environment Topology wizard pick PostgreSQL as the database I want to use. In case I want to get a database cluster just slide to the right the Auto-Clustering switch. Then add a Public IPv4. After that enter an environment name, for example, remotepostgres, and click Create button.
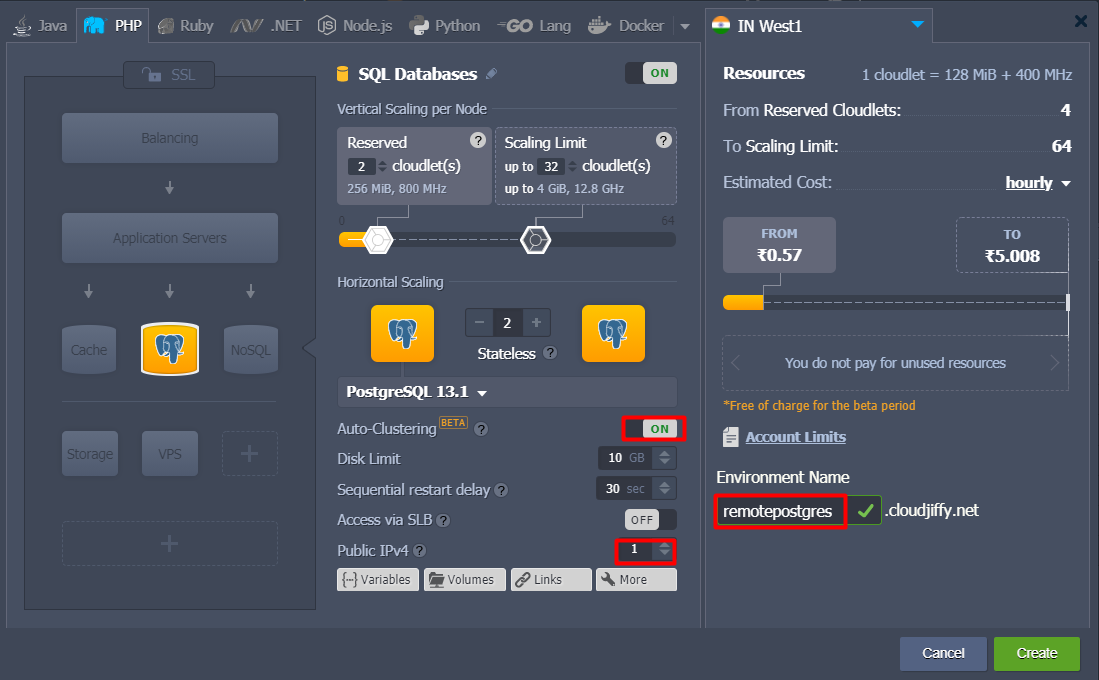
It can take about a minute for creating my environment.
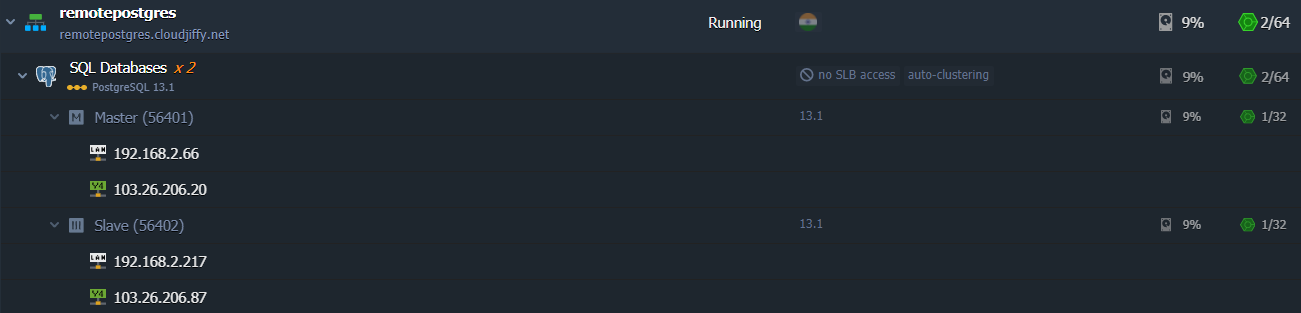
Both nodes have the public IP addresses attached to.
Environment without Public IP
The algorithm is the same as above and clustered database environment will be created but with no public IP attached.
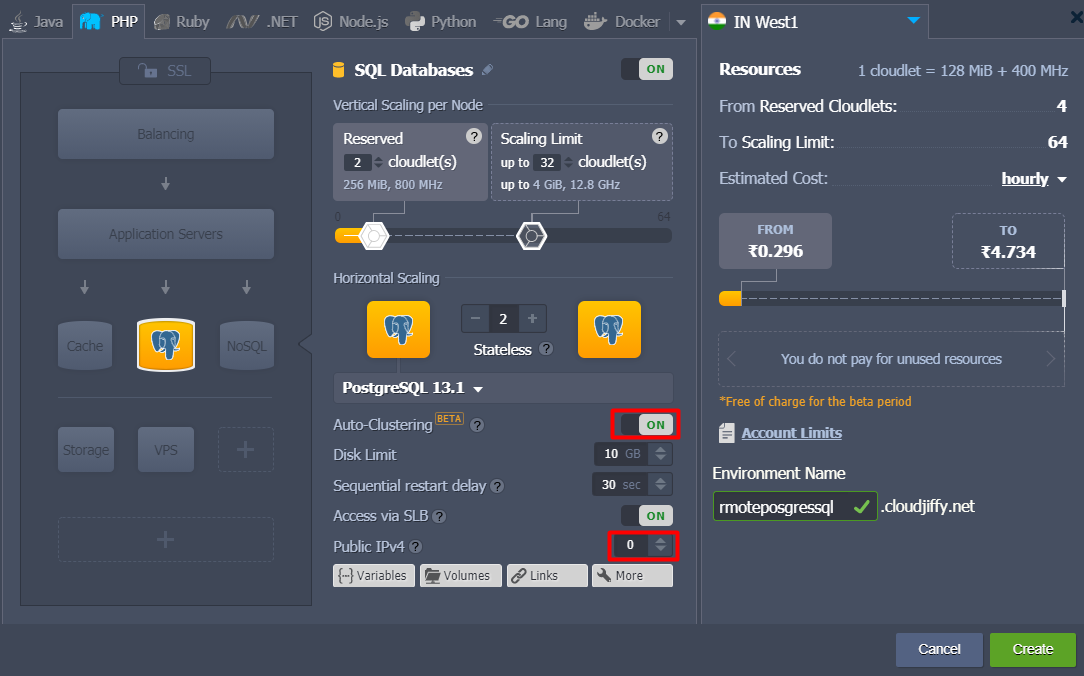
Once the environment is ready, go to the Endpoints at the Settings section and click on Add to create new port mapping.
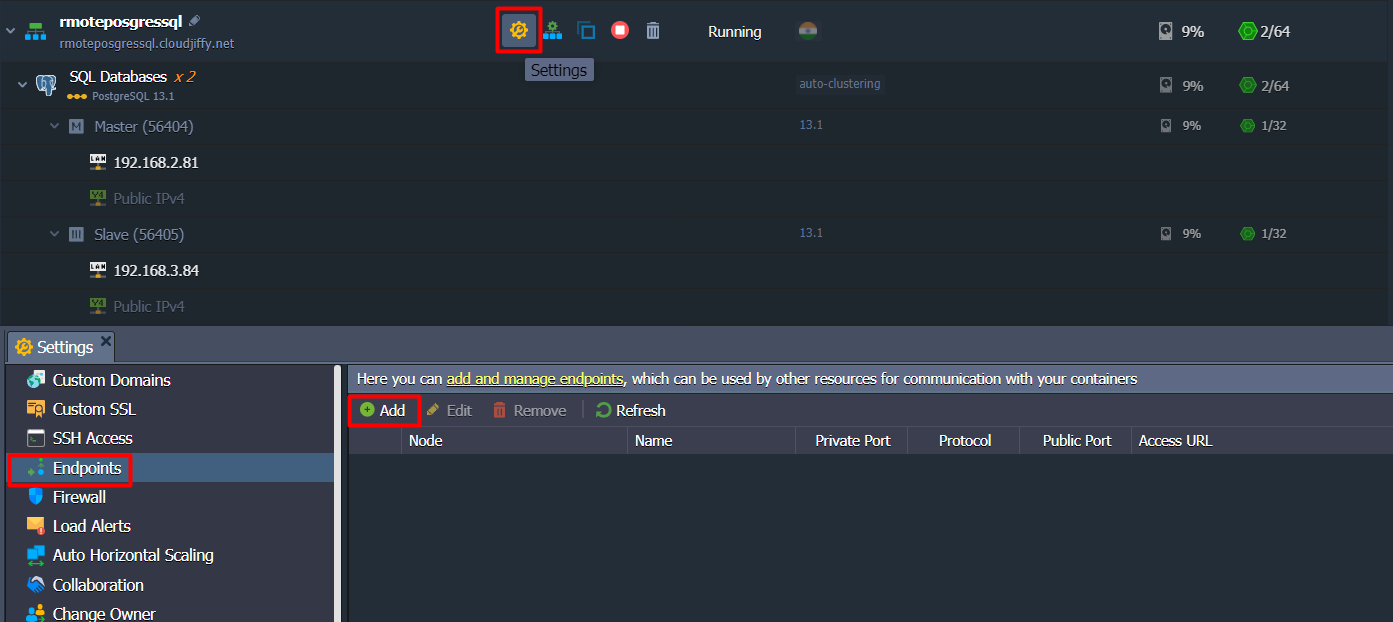
Choose the Node that I need to access and PostgreSQL service Name. The rest parameters will be generated automatically: Private Port, Protocol, Public Port, and Access URL.
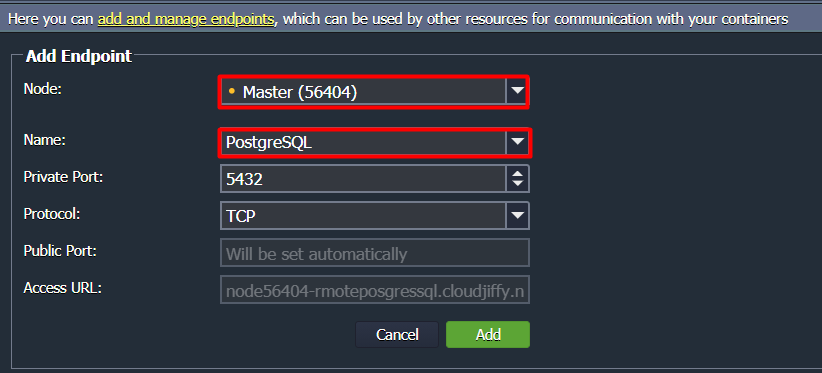
A port mapping to the database master node may look like this.
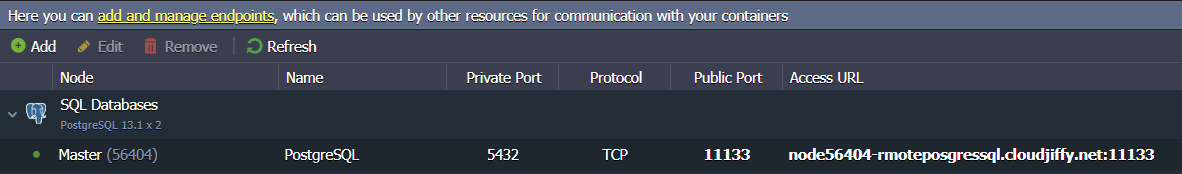
If necessary do the same for the Slave node of the database cluster.
Remote Connection to PostgreSQL
Let’s create a new connection to the database using any desktop or web client. Here we use the pgAdmin4 which is the most popular and feature-rich Open Source administration and development platform for PostgreSQL. I can get client software that meets my platform. See the download page to get the proper link (https://www.pgadmin.org/download) or I may get familiar with this application in Cloudjiffy by deploying it via import of corresponding pgAdmin4 manifest.
- If I have a database cluster it will be more convenient to create a group of all servers that belong to the cluster.
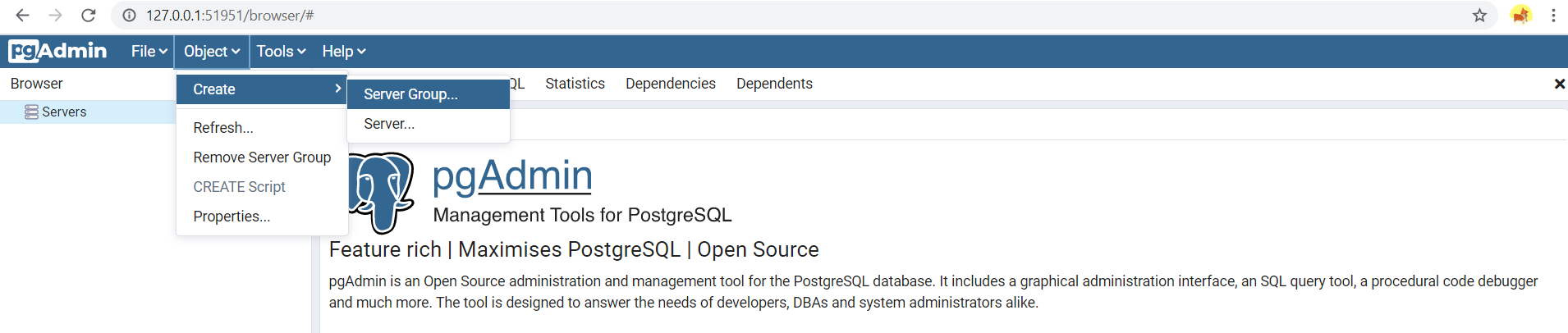
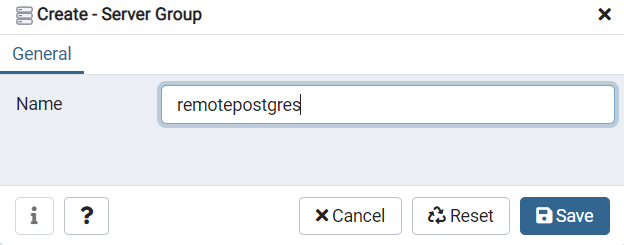
- Then enter Name of the group e.g. remotepostgres.
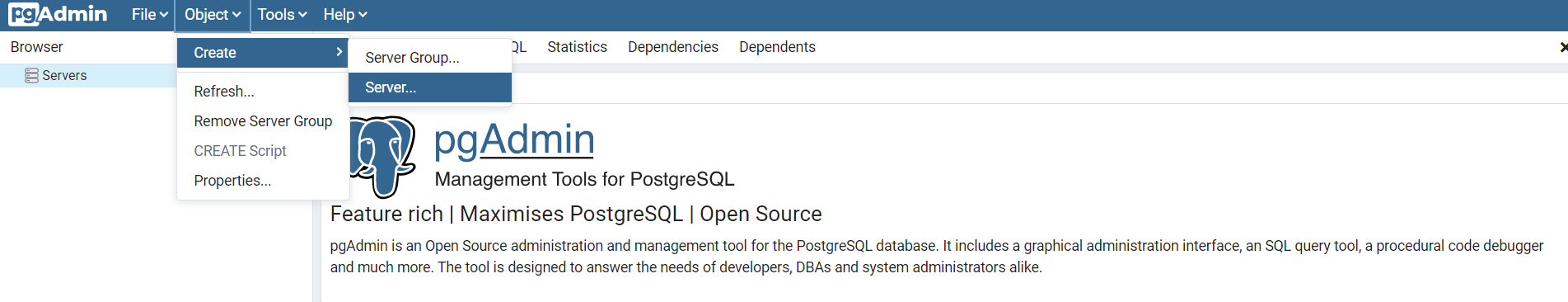
- After that add one by one all of the database servers to the group. Let’s see how to do that for the Master database. Make a right-click on the group (e.g. remotepostgres) and choose Create > Server.
- Enter the server name (e.g. Master for the primary database of my cluster) at the General tab.
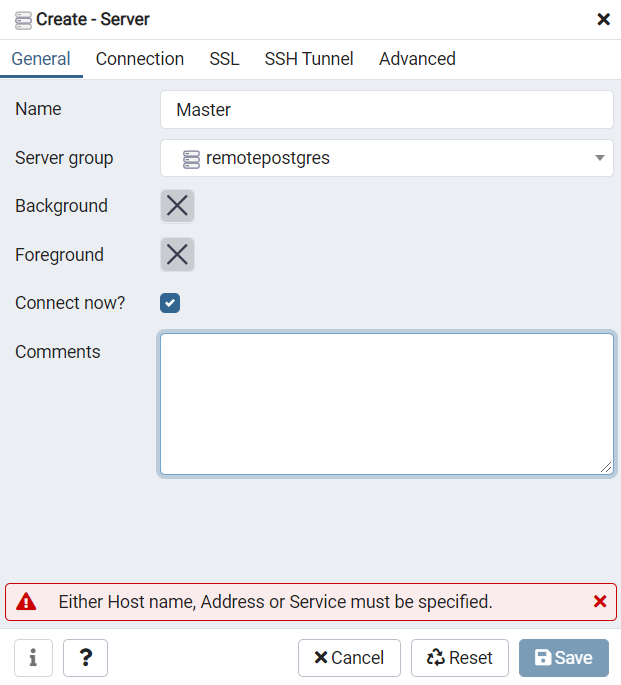
- At this step I have to specify server access settings depending on whether I created database with or without public IP as described above.
Connection to Public IP
Go to the Connection tab and enter public IP of my master database at the Host name/address field. Specify Username and Password I have obtained while creating the database environment via email.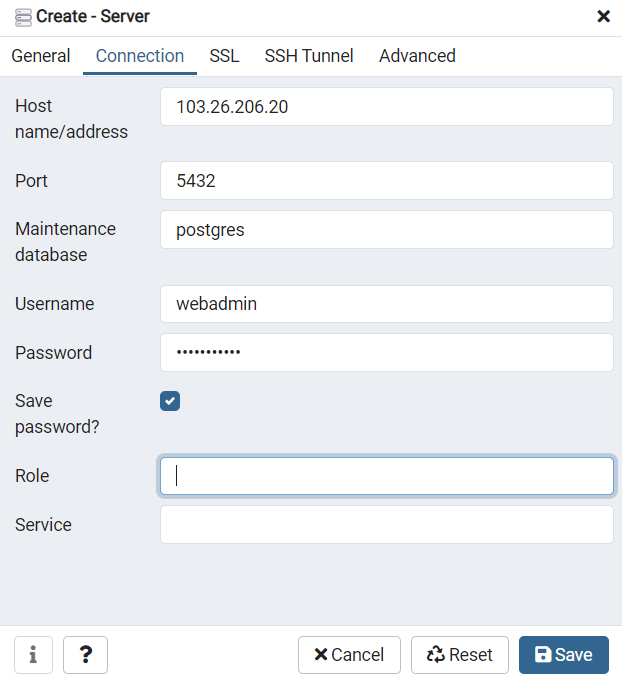
Connection via Endpoints
Take the URL and Public Port from generated port mapping and set the database server connection settings. The Username and Password are the same as described above.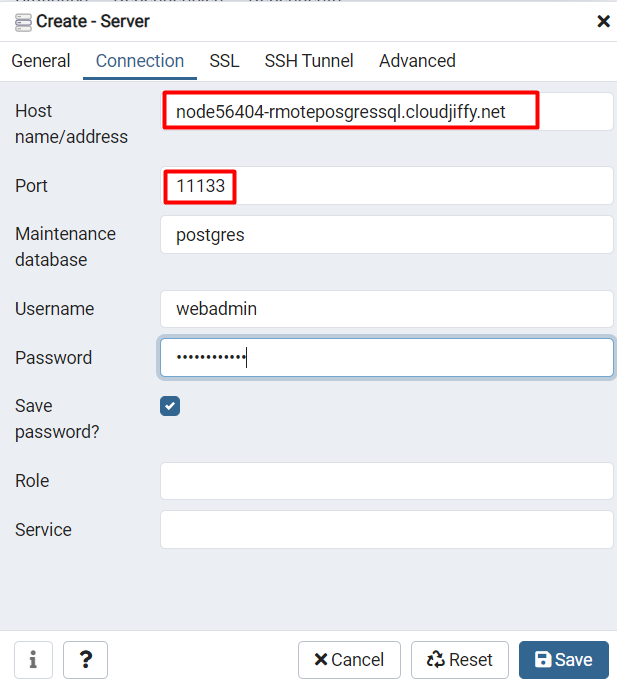
-
I may change other specific options if I rather confident in my actions.
-
Finally, press the Save to apply the changes and I will see that connection is successfully established.
As for our example, both master and slave databases are displayed as follows:
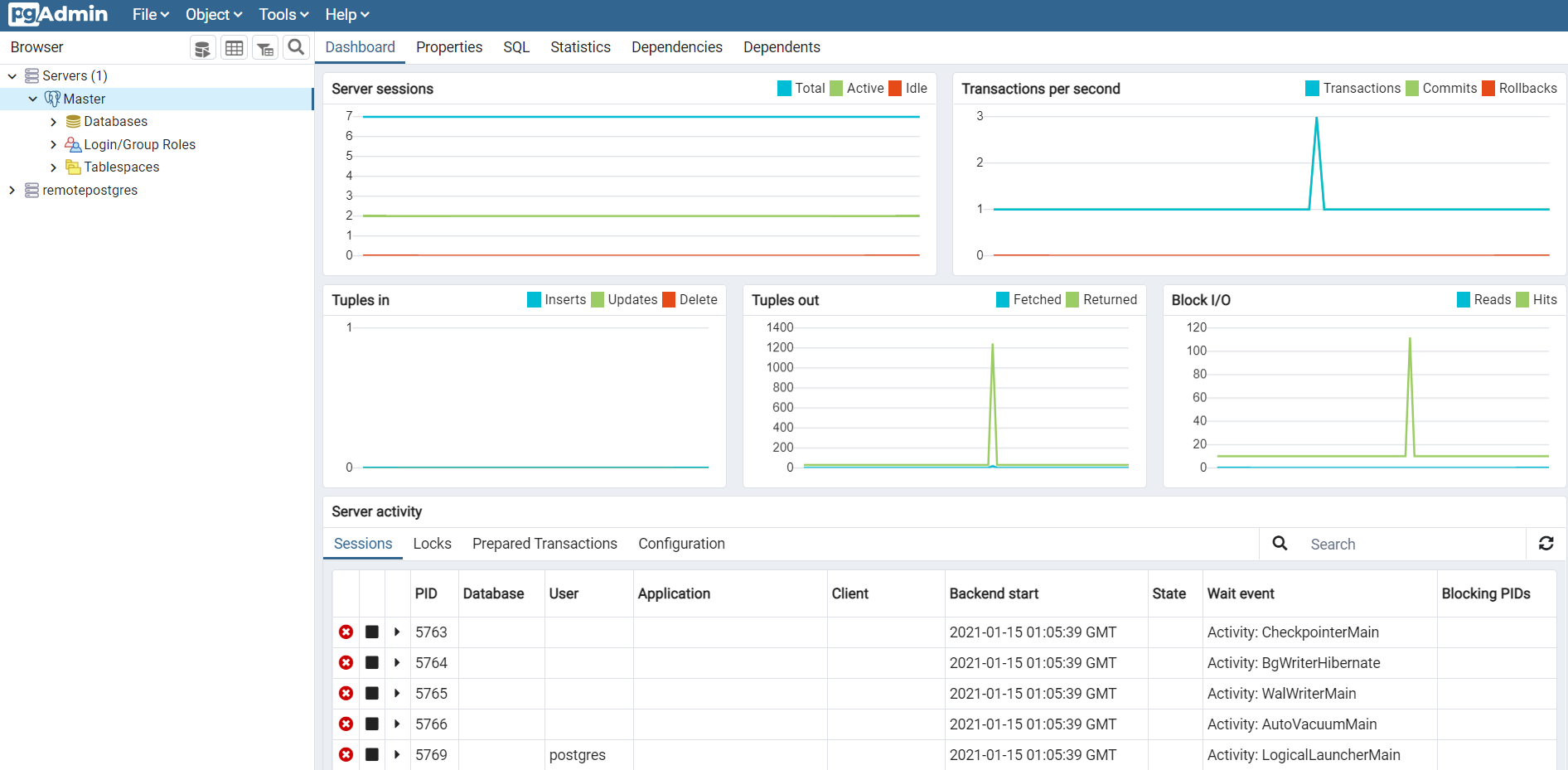
Now PostgreSQL remote access is configured and I can start querying.